【目录】
第1章 词汇语法技巧指南
1.1 大纲要求和试题类型
1.2 词汇语法考点归纳
1.3 答题技巧与备考建议
第2章 词汇语法高分特训1200题
2.1 多项选择填空
◇名词及名词词组
◇动词及动词词组
◇形容词、副词及词组
◇介词及介词词组
◇语 法
2.2 多项选择替换
◇名词及名词词组
◇动词及动词词组
◇形容词、副词及词组
◇介词及介词词组
2.3 改 错
2025年翻译硕士(MTI)《211翻译硕士英语》词汇语法高分特训1200题
【内容节选】
第1章 词汇语法技巧指南
1.1 大纲要求和试题类型
全国翻译硕士专业学位教育指导委员会根据《全日制翻译硕士专业学位研究生指导性培养方案》以及培养高层次、应用型、专业性口笔译人才的教育目标,制定了全日制翻译硕士专业学位研究生入学考试大纲,其中,《翻译硕士英语》考试大纲对词汇语法部分的具体要求如下:
1 考核要求
1)词汇量要求
考生的认知词汇量应在10,000以上,其中积极词汇量为5,000以上,即能正确而熟练地运用常用词汇及其常用搭配。
2)语法要求
考生能正确运用外语语法、结构、修辞等语言规范知识。
在了解该部分的大纲要求时,有两点内容需要注意:
一是词汇量要求。《翻译硕士英语》大纲要求考生的认知词汇量应在10,000以上,其中积极词汇量为5,000以上,即能正确而熟练地运用常用词汇及其常用搭配。而《高等学校英语专业英语教学大纲》对英语专业第四学年的教学要求为通过课堂教学和其他途径认知词汇达10,000-12,000个;且能正确而熟练地使用其中的5,000-6,000个及其最常用的搭配;英语专业八级考试要求词汇量在13,000左右,由此可见,对于英语专业考生《翻译硕士英语》的词汇量要求并不高,为高等学校英语专业本科生经过大学阶段的英语学习与实践应当达到的最低标准。而根据《大学英语课程教学要求》,大学阶段非英语专业的英语教学要求分为三个层次,即一般要求、较高要求和更高要求。更高要求推荐词汇量为约7675个单词,约2360个积极词汇,而大学英语六级词汇范围不超出《大学英语课程教学要求》中较高要求的词汇,即6395个单词,220个积极词汇。所以,如果是非英语专业考生报考翻译硕士,则词汇量要求相对较高,复习的力度应相应加大。
二是语法要求。《翻译硕士英语》大纲要求考生能正确运用外语语法、结构、修辞等语言规范知识。大纲没有指出具体内容,为了使考生能够更加明确复习范围,我们可以把《高等学校英语专业英语教学大纲》对语法要求的具体规定作为参考:能识别词类;区分名词的可数性和不可数性、可数名词的单、复数形式;基本掌握各种代词的形式与用法、基数词和序数词、常用介词和连词、形容词和副词的句法功能、比较级和最高级的构成及基本句型、冠词的一般用法;了解动词的主要种类、时态、语态及不定式和分词的基本用法、句子种类、基本句型和基本构词法;掌握主谓一致关系、表语从句、宾语从句、定语从句和状语从句等句型、直接引语和间接引语的用法、动词不定式和分词的用法、各种时态、主动语态、被动语态和构词法;熟练掌握主语从句、同位语从句、倒装句和各种条件句;较好地掌握句子之间和段落之间的衔接手段如照应、省略、替代等;熟练地使用各种衔接手段,连贯地表达思想。
而对于修辞,《高等学校英语专业英语教学大纲》中并未列出具体需要掌握的修辞手法,下面我们归纳总结了大学英语精读教材中经常出现的一些修辞手法,这些手法主要有simile(明喻)、metaphor(隐喻)、allusion(引喻)、metonymy(换喻/转喻)、synecdoche(提喻)、personification(拟人)、onomatopoeia(拟声)、parody(仿拟)、hyperbole(夸张)、irony(反语)、rhetorical
question(反问)、repetition(反复)、symbolism(象征)、pun(双关)、sarcasm(讽刺)、ridicule(嘲弄)、euphemism(委婉语)、anti-climax(渐降)、understatement(低调陈述)、parallelism(平行/排比)、antonomasia(换称)、antithesis(对照)、transferred
epithet/hypallage(移就)、zeugma(轭式搭配)、alliteration(头韵)、assonance(类韵)、oxymoron(矛盾修辞法)、syllepsis(一语双叙)等。
2 试题类型
多项选择或改错题。
通过对各大院校《翻译硕士英语》考研真题分析可知,词汇语法部分出题形式主要为30个多项选择题,每题1分。词汇题和语法题所占比例不固定,有的院校侧重词汇考察(如对外经济贸易大学),有的院校侧重语法考察(如南开大学)。词汇语法题每题的分值最大为1.5分(如四川大学),最小为0.5分(如厦门大学)。少数院校还会涉及改错(如厦门大学)、修辞(如中南大学)等出题形式。
1.2 词汇语法考点归纳
通过对各高校“翻译硕士英语”词汇语法部分分析研究,我们对词汇语法的常考点进行归纳。
一、语法
“翻译硕士英语”常考语法点有:虚拟语气、非谓语动词、动词时态语态、定语从句、情态动词、比较句型、倒装句、强调句型、状语从句。
(一)虚拟语气的用法
A. 条件从句类
(1)if引导的从句类
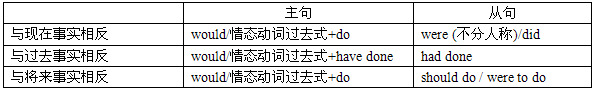
(2)混合虚拟条件类
混合时态的虚拟指的是主句和从句分别表示两个时态,动词形式依照上述三种形式进行相应的变化。
如:If you had done your homework, you would not be criticized by your teacher now.
(3)含蓄虚拟条件类
含蓄虚拟语气是指假设条件不通过if从句表达,而是暗含在其他结构中。考生应熟悉:
①连词but, but that, or, or else;副词otherwise, unfortunately等表示转折假设。
如:A safety analysis would have identified the target as a potential danger. Unfortunately, it was never done.
②介词短语暗含假设条件,常用的有:without, but for, under more favorable conditions等。
如:But for the English examination I would have gone to the concert last Sunday.
③intended/meant/hoped/wished或was/were +不定式完成式或had intended/meant/planned/hoped/wished+不定式一般式暗示虚拟语气。
如:I intended to have called on you, but I was busy at that time.
④情态动词完成式暗示虚拟语气。
如:I should have called to make an airline reservation, but I didn’t.
B. 从句中的 (should) do句型类
(1) 动词suggest,propose,ask,command,demand,require,urge,order,recommend,insist, prefer等后加that引导的宾语从句中使用should do句型。(suggest,recommend和insist分别当“表明”“推荐”和“坚持认为”讲时不用虚拟语气。)
如:In the past men generally preferred that their wives work in the home.
(2) 由上述动词派生来的名词后加that引导的同位语从句或表语从句中用should do句型。
如:It is urgent that these files should be printed right away.
(3) 当上述动词的过去分词及下列形容词strange,important,necessary,essential,urgent,natural,unusual,advisable,desirable,vital等用于句型It is…that中时,that引导的从句中用should do句型。
如:They keep telling us it is of utmost importance that our representative be sent to the conference on schedule.
C. 固定句型类
以下所列单词或短语后所引出的从句,如果是现在的情况,要用一般过去时;如果是过去的情况,要用过去完成时。
(1) It is about/high time(that)“是……时间了”
如:It is high time that we handed in the homework.现在是我们该交作业的时候了。
(2) would rather “宁愿……”
如:Mary would rather she had not broken the window. 玛丽真希望她自己没有打破这个窗户。
(3) wish“希望……”
如:We wish that he could be with us tomorrow.但愿他明天和我们在一起。(对将来的虚拟)
I wish they were at home this time. (对现在的虚拟)
I wish I hadn’t hurt him so much. (对过去的虚拟)
(4) If only“要是…就好了”
例如:If only I were twenty years old. 我要是二十岁就好了。
(5) as if/though“仿佛,好像…”
如:They were sitting there as if nothing had happened. 他们只是坐在那里就像什么事都没发生过。
例:______ before we leave the day after tomorrow, we should have a wonderful time together.
A. Had they arrived
B. Would they arrive
C. Were they arriving
D. Were they to arrive
【答案】D查看答案
【解析】省略if的条件的虚拟语气。此句为if引导的虚拟语气从句,省略if时从句要倒装。当表示对未来事情的虚拟时,从句用should/were to+动词原形,主句用would/should+动词原形。
(二)非谓语动词的用法
非谓语动词的各种用法是考博英语考试中对语法项目要求中非常重要的一项,它包括三种形式:不定式(infinitive),动名词和分词。非谓语动词之所以得名,是因为它不能独立作谓语,不受主语的人称和数的限制,但仍然具有动词的某些特征,在句中可充当主语、宾语、定语、状语及补语等。
1 不定式
不定式在句中可担任除谓语以外的所有成分,即主语、宾语、宾补、表语、定语和状语。
1) 作主语
如果作主语的不定式较长而谓语较短时,常用 it 作形式主语。
To finish the work within three days is impossible.
It is impossible to finish the work within three days.
2) 作宾语和宾补
We have decided to leave next week.
She called me to go back home at once.
①有些动词只能以不定式作宾语,主要有:afford, agree, arrange, ask, attempt, beg, care, choose, claim, dare, decide, determine, expect, fail, hope, intend, learn, manage, mean, need, offer, plan, prepare, pretend, promise, refuse, seek, tend, volunteer, want, wish 等。
I cannot afford to buy such an expensive car.
②不定式作宾语其后又接宾补时,常用 it 作形式宾语,而将不定式放到宾补后面。
I found it impossible to get everything ready in time.
③不带 to 的不定式:在 let, make, have, see, hear, listen to, look at, feel, observe, watch, notice 等动词后,作宾补的不定式不带 to。但是,在被动语态中,不定式要带 to (此时不定式作主补)。
He made his son read the text loudly.
His son was made to read the text loudly.
2 动名词
动名词主要起名词作用,可在句中作主语、宾语和表语,也可作介词宾语。
1) 作主语
在“It is no use (good) doing...”句型中,常用 it 作形式主语,而将作主语用的动名词短语放在后面。
如:It is no good leaving today’s work for tomorrow.
2) 作宾语
①有些动词只能以动名词作宾语,常见的有:admit, avoid, consider, deny, enjoy, endure, fancy, finish, forbid, imagine, mind, miss, permit, postpone, practice, require, risk, stop, suggest 等。
如:The hostess would certainly enjoy receiving the item as a gift.
②有些动词短语也要求动名词作宾语,常见的有:can’t help, feel like, give up, keep on, object to, put off 等。
如:I couldn’t help wondering what this was all about.
3) 动名词的逻辑主语
动名词的逻辑主语通常是句子的主语。动名词的逻辑主语与句子主语不一致时,应有自己的逻辑主语,其形式是:人称代词或名词的所有格+动名词。
如:He was annoyed at my interrupting him.
4) 动名词的完成形式和被动形式
①动名词的完成形式:having + 过去分词,表示动名词的动作发生在谓语动作之前。
如:He regretted not having taken the doctor's advice.
②动名词的被动形式:being + 过去分词,表示动名词的动作与其逻辑主语的关系是被动的。
如:They were afraid of being rejected because of their condition.
5) 动名词与不定式作宾语的区别
有些动词既可以动名词又可以不定式作宾语,且意思差别不大,但有些动词以动名词或不定式作宾语时,意思有较大差别。如:
①remember to do 记得要做(某事)/remember doing 记得曾做过(某事)
②forget to do 忘记要做(某事)/ forget doing 忘记曾做过(某事)
③go on to do (做完某事后)继续做(另一事)/ go on doing 继续做(某事)
④regret to do 对要做(某事)感到遗憾 / regret doing 对已做过(某事)感到后悔
⑤need to do 需要做(某事)/ need doing 需要(被动)
3 分词
分词有现在分词和过去分词两种。现在分词表示主动、进行的意义;过去分词表示被动、完成的意义。如:boiling water (water which is boiling),沸水;boiled water (water which has been boiled),开水。分词主要起形容词和副词作用,在句中作表语、定语、宾补(主补)和状语等。
1) 作定语
分词作定语时与被修饰的词有逻辑上的主谓意义。分词短语作定语时,置于被修饰的词之后。
如:Most of the computers are small machines sitting on (= which sit on) the desks.
There are all sorts of computers connected to (= which are connected to) the Internet.
2) 作宾补(主补)
宾语与宾补有逻辑上的主谓意义。常以分词作宾补的动词有:catch, have, keep, get, see, hear, find, feel, leave, make, want, start, notice, observe, watch, set 等。
如:The policeman caught the young man stealing from the shop.
Libraries often have computers connected to the Internet for members of the public to use.
3) 作状语
①表示时间,多置于句首,注意如果分词表示的动作的时间先于谓语动词,要用完成式。
如:Having completed one task, we started on another one. (complete先于start之前发生)
②表示原因,置于句首句尾均可,根据情况有时要用完成式,有时用一般式。
如:There seemed little hope that the explorer, having been deserted in the tropical forest, would find his way through it.
③表示伴随、方式,置于句尾,用分词的一般式。
如:Helen borrowed my dictionary the other day saying that she would return it soon.
Anna was reading a piece of science fiction, completely lost to the outside world.
④表示结果,置于句尾。
如:European football is played in 80 countries, making it the most popular sport in the world.
⑤表示补充说明(同位),置于句尾,用分词的一般式。
如:The article opens and closes with descriptions of two news reports, each making one major point in contrast with the other.
⑥表示条件
如:Weather permitting, we’ll go to the Great Wall tomorrow. 天气允许的话,我们就会去长城。
4) 分词的独立主格结构
分词的逻辑主语一般为句子的主语,否则分词短语要有自己的逻辑主语,称为分词独立主格结构。分词独立主格结构只是句子的一个部分。
如:All flights having been canceled because of the snowstorm, we decided to take the train.
Darkness setting in, the young couple lingered on merrymaking.
5) 现在分词的完成形式和被动形式
① 现在分词的完成形式:having + 过去分词,表示分词的动作发生在谓语动作之前。
如:Having been there many times, she is quite familiar with the city.
② 现在分词的被动形式:being + 过去分词,表示分词的动作正在发生,或与谓语动作同时发生,但与主语的关系是被动的,作状语时相当于过去分词。
如:The person being interviewed is my former classmate.
(Being) bothered by the noise, he could not concentrate himself on his work.
③ 现在分词的完成被动形式:having + been + 过去分词。
如:Having been rebuilt, the palace looks more splendid.
例 1:______, the guest speaker was ushered into the auditorium hall to give the lecture.
A. Being shown around the campus
B. Having shown to the campus
C. After been shown around the campus
D. Having been shown around the campus
【答案】D查看答案
【解析】完成时现在分词形式表时间。be shown around the campus这一动作发生在 was ushered in to the auditorium hall之前,应用完成时;另外,由题意可知需要用被动形式。
例 2:Telecommuting is a new form of work ______ to work, such as fathers with children, the chance to work while remaining at home.
A. that affording those unable previously
B. affords those who were previously unable
C. affording those previously unable
D. afforded those previously unable
【答案】C查看答案
【解析】现在分词形式作定语。句意:远程办公是一种新的工作形式,它使得那些以前没办法上班的人(比如有小孩的父亲们)有机会在家里上班。主句是Telecommuting is a new form of work.后面可跟分词短语表伴随,也可跟同位语从句补充说明a new form of work。本题选C,若用从句形式,应为:that affords those who are previously unable…。
(三)时态语态
★ 常考时态
1将来时测试重点
(1) 在时间、条件、让步从句中,一般现在时代替将来时,但要注意区别从句的类型。
如:I’ll tell him when you will ring again. 我告诉他你什么时候再来电话。(宾语从句)
比较:I’ll tell him when you ring again.你再打电话时我告诉他。(状语从句)
(2) 在make sure, make certain, see (to it) 后的that从句中,谓语动词用一般现在时代替将来时。
如:See to it that you include in the paper whatever questions they didn’t know the answer to last time.
2 过去时测试重点
主句谓语动词是过去时态,从句应根据上下文的意思选用相应的过去时态。
①从句的动作与主句动作同时发生,从句用一般过去时或过去进行时。
如:Her father said that she was preparing her lessons yesterday evening.
②从句的动作发生在主句动作之前,从句用过去完成时。
如:The hospital reported that its X-ray machine had failed.
③从句的动作发生在主句动作之后,从句用过去将来时。
如:He thought that his son would phone him as soon as he got there.
注:当从句表示客观事实或真理时,其时态不受主句谓语时态的影响,总是用一般现在时。
如:The teacher told the children that the earth always moves around the sun.
3 完成时测试重点
(1) by/between/up to/till +过去时间、since、by the time/when +表示过去发生情况的从句,主句用过去完成时。
如:We had just had our breakfast when an old man came to the door.
(2) by +将来时间、by the time/ when +谓语动词是一般现在时的从句,主句用将来完成时。
如:①By the time you arrive in London, we will have stayed in Europe for two weeks.
②I hope her health will have improved greatly by the time we come back next year.
(3) by now、since +过去时间、in/during/for/over/the past/last few(或具体数字)years/days/months,主句用现在完成时,但在it is +具体时间since/before这一句型中,主句更多的时候不用完成时。
如:①The changes that had taken place in air travel during the last sixty years would have seemed completely impossible to even the most brilliant scientists at the turn of the 19th century.
②It is four years since John left school.
(4) 在It is the +序数词/形容词最高级+that的定语从句中,谓语动词常用现在完成时。
如:It isn’t the first time that I have found myself in an embarrassing situation.
(5) 在no sooner…than…, hardly/scarcely…when…句型中,主句常用过去完成时。
答题思路:先根据选项的区别点确定考题要点为时态,然后回到题句中寻找给出的或暗示的时间状语,缩小选择范围,进而选出正确答案;
★ 语态
确定主语与谓语之间的关系是正确应用语态的关键。主动语态表示主语是谓语动作的执行者;被动语态表示主语是谓语动作的承受者。不及物动词及表示状态的动词无被动语态。
如:They must finish all the work before March. (SVO)→ All the work must be finished (by them) before March.
1) 主动语态的句子中,如宾补是不带 to 的不定式,当句子变成被动语态后,由宾补变为主补的不定式必须带to。
如:The teacher made us write business letters in English. → We were made to write business letters in English.
2) 带有主语从句的被动语态,常用形式主语 it,将主语从句后置。
It is said that...
It is reported that...
It has been proved that...
注:时态和语态经常合在一起考。
例:How can I ever concentrate if you ______ continually ______ me with silly questions? [2008年真题]
A. have, interrupted
B. had, interrupted
C. are, interrupting
D. were, interrupted
【答案】C查看答案
【解析】句意:如果你一直问我如此愚蠢的问题、打扰我,我怎么能集中注意力干事呢?因为是这一段时间一直受打扰,所以用现在进行时。
(四)定语从句
定语从句所修饰的先行词可以是名词或代词,也可以是一个句子。定语从句通常位于先行词之后,由关系代词或关系副词引导。
1 限制性定语从句
限制性定语从句修饰先行词,对先行词起限制作用,紧接先行词之后,无逗号,若省去,原句意思不完整。引导定语从句的关系代词有 who, whom, whose, which, that 等。who, whom, whose 用于指人,whose 有时也可指物,相当于 of which; which 用于指物;that 既可指人,也可指物,但只用于限制性定语从句中。关系代词除了引导定语从句,替代先行词外,还在从句中担任主语、宾语、定语等。
The computers and cables which make up the Internet are owned by people and organizations.
Those who live alone or who are sick may have trouble in getting close to other people.
The girl whose parents died in an accident is living with her grandmother.
(1)当先行词是all, anything, everything, something, nothing 等不定代词,或先行词前有 first, last, any, few, much, some, no, only 以及形容词最高级修饰时,只能用关系代词 that 引导定语从句。
That is all that I have heard from him.
He is the first person that I’m going to interview this afternoon.
(2)关系代词的省略:在从句中作宾语的关系代词常可省略。关系代词紧跟介词,作介词宾语时不可用that,只可用which 或whom 引导从句,并且不可省略,但当介词位于定语从句句末时,作为介词宾语的关系代词仍可用 that,也可省略。
This is one of those things with which we have to put up.
This is one of those things (which / that) we have to put up with.
(3)引导定语从句的关系副词有 when, where, why 等。关系副词在从句中作状语,意义上相当于一个“介词 + which”的结构。
Even in comic books where (= in which) there are no words, the stories are fully expressed through the drawings.
No one knows the reason why (= for which) he was so angry that day.
2 非限制性定语从句
非限制性定语从句既可修饰先行词,也可修饰整个主句,起补充说明作用,与主句之间有逗号隔开,若省去,原句意思不受影响。不可用 that 引导非限制性定语从句。关系词不可省略。
Every object has a gravitational pull, which is rather like magnetism.
3 “介词 + which / whom / whose”引导的定语从句
“介词 + which / whom / whose”可引导限制性的定语从句,也可引导非限制性定语从句,该结构中介词的选择取决于从句谓语动词的固定搭配,或先行词的习惯搭配。
This is the computer on which he spent all his savings.
4 as 引导的定语从句
as引导的定语从句主要用于“such...as”及“the same...as”的结构中,代替先行词是人或物的名词。as 引导非限制性定语从句时,代替整个主句,从句可位于主句之前、之后或中间。
These are not such problems as can be easily solved. ( as代替先行词 problems)
例:______ is often the case with a new idea, much preliminary activity and optimistic discussion produced no concrete proposals.
A. That
B. It
C. This
D. As
【答案】D查看答案
【解析】as引导的非限制性定语从句。句意:正如一种新的观念产生时一样,人们总是做许多准备活动和积极的讨论,却拿不出具体的建议。as作关系代词,引导非限定性定语从句,表达整个主句的意思。非限定性定语从句的作用是对所修饰的成分作进一步说明,通常和主句间用逗号隔开,将从句拿掉后其他部分仍可成立。
(五)情态动词的用法
在北大考博英语考试中,情态助动词是常考的项目。尤其是情态动词+动词完成体的结构,用来表示对过去的行为或动作进行推测或评论。常见的有如下结构:
1 must have done
表示对过去事实肯定的猜测,意为“一定发生了”。
如:Since the ground is wet,it must have rained last night.
在表示否定的猜测时,即当意思为“一定没发生”时,用can not/could not have done结构。
2 could/may/might have done
表示“很可能、或许发生了”,表示不太肯定的推测。其中might have done表示事情“本来可能而事实却未发生”。
3 should/ought to have done
表示事情“本来应该发生而事实上却未发生”。相应的,此结构的否定式表示事情“本来不应该发生而事实上却发生了”。
4 needn’t have done
是对过去事情的必要性的否定,表示“本不必而事实上却发生了”;而对过去事情的必要性的否定还有一种方式,即didn’t need to do,此结构表示“不必发生而且也没有发生”。例如:
It is Sunday today, you needn’t have gone to school! (言下之意是去学校的动作已经发生了。)
(六)比较句型
1 not so much…as…与其说…不如说…
如:The chief reason for the population growth isn’t so much a rise in birth rates as a fall in death rates as a result of improvements in medical care.
2 no/not any more…than…两者一样都不…
如:The heart is no more intelligent than the stomach, for they are both controlled by the brain.
3 no /not any less…than…两者一样都…
如:She is no less beautiful than her sister.
4 just as…so….正如…,…也…(用倒装结构)
如:Just as the soil is a part of the earth, so is the atmosphere.
5 A is to B what C is to D, A对B而言正如C对D一样
6 The –er, the –er, 越…越…
例:The most interesting new cars may owe ______ the simple wisdom of hiring a few talented people and allowing them to work.
A. less local free-spiritedness than
B. less local free-spiritedness than to
C. to less local flee-spiritedness than to
D. less to local free-spiritedness than to
【答案】D查看答案
【解析】考查less…than…的比较句型。句意:这些新型有趣的车(的出现)与其说归功于当地自由和活跃的气氛,还不说是聘用少数几个人才并能允许他们放手去干的这份睿智。owe to归功于。
(七)倒装句
根据主语和谓语在句中的位置,倒装句可分为完全倒装和部分倒装。完全倒装指整个谓语置于主语之前。部分倒装指谓语的一部分置于主语之前,通常是将助动词或情态动词提前。
1 当句首为 here, there, up, down, away, now 等副词,谓语动词为 be, go, come, fly 等时,主谓要完全倒装,但主语若是人称代词,则主谓不用倒装。
如:There goes the bell.
2 否定词或带有否定意义的短语位于句首时,要倒装,如 hardly, never, rarely, seldom, not only...but also, in no way, at no time, in no case, by no means, no sooner...than, neither...nor, hardly...when, under no circumstances, on no account 等。
如:Rarely would any of us stand up and show the world who we are.
3 “only + 状语”位于句首时,要倒装。
如:Only in this way can we solve the problem.
4 在 so / such...that 结构中,so / such 位于句首时,要倒装。
如:So clear was the statement that it couldn't be misunderstood.
Such was his kindness that I will never forget him.
例:He is not under arrest, ______ any restriction on him.
A. or the police have placed
B. or have the police placed
C. nor the police have placed
D. nor have the police placed
【答案】D查看答案
【解析】考查nor引导的部分倒装句。句意:他没有被捕,警察也没有对他(的行为)进行限制。在同一个句子中,主语相同,都是he,可以排除选项A和C。而由于前半句为否定,后半句也应该使用表示否定意义的nor。
(八)强调句型
1 强调句的基本句型:It is / was + 被强调的句子成分 + that / who + 句子的其他成分。
如:It was Doctor Smith that (who) gave us a lecture last week.
2 在肯定句中,可用“do (does, did) + 原形动词”来强调谓语动词。
如:Millions of Americans do get some enjoyment from watching television.
3 有些单词和词组在句中起强调作用,常见的有only, even, just, ever及反身代词等。
如:I was the first one ever in my family to go to college.
4 注意区分 it 引导强调句型和it作形式主语替代主语从句:在强调句中,it不替代任何句子成分,如果将强调结构“It is...that / who...”去掉,句子可还原,而在主语从句中,it 替代主语从句,只要将it去掉,句子就可还原。
It was in my bag that I found the book. (强调句型)→ I found the book in my bag.
It was quite obvious that he did much better than you. (it 引导主语从句) → That he did much better than you was quite obvious.
(九)状语从句
状语从句可细分为:时间、地点、条件、原因、让步、目的、结果、比较、方式等。
状语从句的测试重点为:考查考生对主从句之间逻辑意义关系的把握,看其是否能选择正确的从属连词。
1 条件状语从句的常考知识点
复合连词as long as,so long as,as far as,on condition that,in the event that;动词及分词provided(that),providing(that),given that, suppose/supposing(that),assuming,say等引导条件状语从句。如:
You can arrive in Beijing earlier for the meeting provided you don’t mind taking the night train.
Assuming he is diligent in his studies at ordinary times, he is sure to pass the test.
In the event that she has not been informed, I will tell her. (如果…)
You can go swimming on condition that you don’t go too far from the river bank. (如果…)
Suppose it rained, we would still go. (假如…)
Say it were true, what would you do about it? (假如…)
2 让步状语从句的常考知识点
1) as 引导让步从句,要求用倒装结构,把强调的部分置于句首。如:
Much as he likes her, he does get irritated with her sometimes.
Humble as it may be, there is no place like home.
2) 复合连接词for all that和分词granting/granted(that)引导让步从句。如:
Granted you have made much progress, you should not be conceited.
For all that computers can provide us with great help, they shouldn’t be seen as substitutes for fundamental thinking and reasoning skills.
3 时间状语从句的常考知识点
1) before表示汉语的“只有/必须…才能”。
2) when引导时间从句时,如果出现在后半句,则表示“这/那时突然”。
3) when it comes to 是习惯用法,意为“当谈到…时”。如:
4) 名词短语、介词短语each /every time, the moment/second/minute, in the time, by the time起连词作用。
5) 副词directly, immediately, instantly, now引导时间从句, 相当于as soon as。
4 原因状语从句的常考知识点
1) in that引导原因从句时,有时翻译成“是因为”、“就在于”。如:
2) now that表示“既然”;seeing that, considering表示“鉴于”、“考虑到”。如:
其他引导原因状语从句的连接词语还有: for the (simple) reason that, by reason that, on the grounds that, in as much as, in so far as等。
5 while, whereas 引导对比从句
6 so…that…, with the result that, so much so that 引导结果状语从句
7 in order that, in case, for fear that, lest (用虚拟语气) 引导目的状语从句
例:______ we wish him prosperous, we have objections to his ways of obtaining wealth.
A. Much as
B. As much
C. More as
D. As well as
【答案】A查看答案
【解析】考查as引导的让步状语从句。副词much前置,题意是“虽然我们都希望他富起来,但我们反对他获得财富的方式”。
二、词汇
词汇试题内容主要涉及三个方面:词义辨析、固定搭配及习语使用。
(一)词义辨析
做该类题时须对四个选项进行辨析。根据选项的词形及语义特点,可将其分为近义词、近形词、同源词和纯生词四种类型。
1 近义词
即部分选项或四个选项词义相近,但在词义的内涵和外延、用法以及搭配上有所不同。该类题在考博词汇测试中很常见且极易丢分,而且比重最大。其实质是考查近义词的辨析,检验考生在具体语言环境中的用词能力。由于这些词的差别极其细微,在平时的学习中非常容易被忽视。因此这就要求考生平时就注意每个词的用法及常用搭配。
解答此类题时考生可从三个方面入手:
①从词汇的语法特征入手
考生可以从空格所填词汇的单复数、可数不可数、被动语态、动词的及物不及物等语法特征入手,来辨别近义词。如consist一般用于主动态,而compose常用于被动语态。
②从词义的内涵外延入手
如:alter和convert都表示改变,变更。但是alter指衣服等表面或局部做部分变动,而没有变成另一种事物。convert一般只表示事物的外表及用途等方面发生的次要变化,而不是本质上的巨大变化,也可用于改变某人的政治观点、信仰,这个词义是alter所没有的。
③从搭配习惯入手
如表示“坚持”的insist 和persist 的差别就在于搭配不一样。insist后面需用介词on。persist后面需用介词in。
例 1:I couldn’t sleep because the tap in the bathroom was ______.
A. draining
B. dropping
C. spilling
D. dripping
【答案】D查看答案
【分析】句意:浴室水龙头滴水,害得我睡不着。水龙头滴水用drip。drain排(水),泄(水)。drop放下,掉下。spill溢出,洒,使...流出。
例 2:______ springs not out of true and deep admiration, but more often out of a self-seeking wish to identify with someone important or famous.
A. A compliment
B. An adulatory
C. Flattery
D. Praise
【答案】C查看答案
【解析】题意为:奉承话并非出自真诚的、深刻的钦佩,更多情况下是出自一种利己主义的意愿,希望自己被某个重要人物或名人认同。flattery奉承话,恭维话,谄媚的举动,贬义词;compliment称赞,褒扬,褒义词;adulatory adj.奉承的,谄媚的,吹捧的;praise 赞扬,歌颂。
例 3:Once a picture is proved to be a forgery, it becomes quite ______.
A. invaluable
B. priceless
C. unworthy
D. worthless
【答案】D查看答案
【解析】句意:一旦一幅画被证明是伪造的,这幅画就马上变得没有价值了。invaluable无价的。priceless无价的。unworthy不足道的;不光彩的;不值得的。
2 近形词
该类题的特点是,在四个选项中至少有两个选项拼写相近或是同根词、同缀词,但其意思却截然不同。对于单词掌握不够扎实的同学来说,这类题很容易丢分。解决的方法一是靠平时记忆单词的时候就注意区分对比,二是对于那些同根不同缀或同缀不同根的选项,可以利用词根及词缀的知识进行分析对比。
如:compliment赞美/complement补充;adapt使...适应/adopt采用; inquire打听,询问/ require要求,命令;compel强迫,迫使屈从/impel促成,推动;compress挤压/comprise包括;confirm证实/conform符合;award授予,给予/reward奖赏,报答;ensure保证,担保/insure 给…保险;extinguish熄灭/distinguish 区别,辨别;wander漫游/wonder惊叹;contract缔结,订约/contact使接触;miraculous奇迹的,不可思议的/meticulous一丝不苟的,精确的。
例 1:Nobody knows what triggered the event, which ______ a million cubic meters of water per second, obliterating the barrier between Britain and France.
A. released
B. relieved
C. restored
D. retained
【答案】A查看答案
【解析】四个单词的前缀皆为re-,此前缀表示again再,又,重(可作动词及由动词派生的名词、形容词和副词的前缀)。句意:没人知道是什么导致这起事件发生的,每秒钟释放一百万立方米的水,湮没了英法两国之间的障碍。release释放。relieve解除,减轻。restore回复,归还。retain保持,保留。
例 2:The hospital denies there is any connection between the disciplinary action and Dr. Reid’s ______ about health problems.
A. allegiance
B. alliance
C. allegations
D. alliteration
【答案】C查看答案
【解析】allegation主张,断言。allegiance 忠贞,效忠。alliance 联盟。alliteration头韵。
例 3: Professional archivists and librarians have the resources to duplicate materials in other formats and the expertise to retrieve materials trapped in ______ computers.
A. abstract
B. obsolete
C. obstinate
D. obese
【答案】B查看答案
【解析】此题后三个选项词形十分相近。句意:…有专门技术能够提取出那些储存在不再使用的电脑中的资料。obsolete不再使用的,过时的。abstract抽象的,深奥的。obstinate倔强的,顽固的。obese肥胖的,肥大的。
3 纯生词
所谓纯生词,是指四个选项在形、义上都不相同,因此只有认识备选单词才能选对答案。一般而言,此类词汇题所考单词比较难,所以难度水平较大。该类题在每年的词汇测试中所占比重都不小。解题关键在于读懂题干,然后按照题干提示信息,填入一个最恰当的词,使整句话语法合理、语义通顺。
例 1:In Germany, the industrial giants Daimler Chrysler and Siemens recently ______ their unions into signing contracts that lengthen work hours without increasing pay.
A. muscled
B. moved
C. mushed
D. muted
【答案】A查看答案
【解析】muscle强行挤入以分享利益。mush压碎。mute使减弱(声音)。
例 2:He is ______ drinker, who has been imbibing for so long that he has figuratively speaking, grown old with the vice.
A. an inveterate
B. an incorrigible
C. a chronic
D. an unconscionable
【答案】B查看答案
【解析】题意为:他是个无药可救的酒鬼,酒龄如此长,以至于可以形象地说他将和恶习一起变老。incorrigible无药可救的,不能被纠正的;inveterate成癖的,根深的;chronic慢性的,延续很长时间的;unconscionable不合理的,过度的。
4 同源词辨析
所谓同源词是指有相同词根或词源的单词。
例:We have been hearing ______ accounts of your work.
A. favored
B. favorable
C. favorite
D. favoring
【答案】B查看答案
【解析】此题的四个选项皆为favor的同源词。句意:我们一直以来都听到对你的工作大加赞赏的言辞。favorable令人满意的。favored受到优待的。favorite最喜爱的。favoring有帮助的。
(二)固定搭配题
这类题型的特点是四个选项中有一项能与该句结构中的某(几)个词构成固定搭配或选项本身即为固定短语。在每套试题中,固定搭配题约为5至6道。固定搭配题按选项的性质可分成以下几种类型:常用动词短语、介词短语、副词短语以及其他固定搭配短语。
(1)动词词组
例:Most people can’t get ______ the day without at least one cup of tea or coffee.
A. on
B. through
C. over
D. by
【答案】B查看答案
【解析】句意:白天绝大多数人不喝咖啡或茶就撑不下来。get through度过。get on生活,进展,相处融洽。get over渡过;传送;克制。get by通过,混过。
(2)名词词组
例:Please put your empty cigarette packets and paper bags in the ______ bins provided.
A. junk
B. litter
C. scrap
D. deposit
【答案】B查看答案
【解析】句意:请把空烟盒和纸袋放在垃圾桶里。litter废弃物;litter bin为固定词组,意为“垃圾箱”。junk无用的东西,比如说垃圾邮件和垃圾食品。scrap碎屑,(工业)废料;scrap bin指废弃箱,收纳废片、废纸等的(存放)箱。deposit存款;沉淀。
(3)介词词组
例:As the director can’t come to the reception, I’m representing the company ______.
A. on his account
B. on his behalf
C. for his part
D. in his interest
【答案】B查看答案
【解析】句意:因为主任不能代表公司出席招待会,所以我将代替他参加招待会。on one’s behalf代表某人。for one’s part至于某人,对某人来说。in one’s interest等同in the interest of sb.为了某人的利益。
(4)习语
习语是一些固定的词组,其组成部分不可替换或增减,而且它们的意思也不能从其组成部分推测出来,因此,对习语不能望文生,更不可想当然,要把它当作一个整体来记忆和掌握,其关键在于平时的积累。如:
be at ones wits’ end一筹莫展,黔驴技穷
behind bars 坐牢
get one’s goat 使人发怒或厌恶
card up one’s sleeve锦囊妙计
turn a cold shoulder to对…冷淡
be all ears洗耳恭听
pay lip service假殷勤
a hard nut to crack难对付的人
to rack one’s brain绞尽脑汁
be a notch above略胜一筹
stab in the back背后捅刀子
bear somebody a grudge怀恨在心
plough the air白费力气
blow the whistle告发、检举
give someone the runaround敷衍搪塞
a thorn in someone’s flesh眼中钉
under the weather身体不适,生病
save your breath 省口气吧;别白费口舌了
drag one’s feet行动缓慢
grin and bear 任劳任怨
as fit as a fiddle 非常健康
by hook or by crook 不择手段,无论如何
例:The more people hear his demented rants, the more they see that he is a terrorist ______.
A. who is pure and simple
B. being pure and simple
C. pure and simple
D. as pure and simple
【答案】C查看答案
【解析】句意:听着他狂乱的演说,人们越来越觉得他是个十足的恐怖分子。pure and simple完全的,十足的。
本文内容选自达聪学习网(https://dacai.100xuexi.com/)2025年翻译硕士(MTI)《211翻译硕士英语》词汇语法高分特训1200题
,点在线阅读即可免费试看,持续更新中……
点击获取资料
达聪学习网收录了各类考试真题、笔记、视频等复习资料,考研考证的同学可以点击对应分类寻找适合自己的资料或者直接点击搜索框搜索所需资料关键词查找更多考试相关资料电子书,教材相关试题、历年真题解析,配套题库、考试复习笔记、知识点整理、考点归纳总结、课后习题答案、名校考研真题、网课视频,可以扫描下方二维码关注【达聪学习网】官方公众号获取正版考试资料,网页平板手机均可登陆使用,账号信息、做题记录、重点笔记等多端同步。
以上就是关于“ 2025年翻译硕士(MTI)《211翻译硕士英语》词汇语法高分特训1200题”的内容,更多学习资料、备考经验可以关注【达聪学习网】公众号~

Tip:如何在达聪学习网查找到我需要的资料?
方法一:在达聪学习网顶部搜索框输入您需要的资料关键字(考试名称/科目名称/教材名称等)。即可获得搜索结果。
方法二:在达聪学习网菜单选项中有资料分类,您可以按考试类别查看。
方法三:关注“达聪学习网”公众号,在菜单里点“查找资料”,输入关键词搜索
【上万种考试资料,达聪助你一次通关】
考研考博类
全国547所院校专业课 |考研公共课 |统考专业课 |非统考专业课 |专业硕士 |同等学力申硕 |考博 |一对一 |经典教材 |期末速成
考证考试类
会员VIP
本站题库电子书开通会员VIP即可随心看,对于考试/所需资料较多的同学可以考虑直接开通会员VIP,有任何疑问也可以点击咨询按钮找学习顾问给您解答~